A robotic arm successfully learnt 1,000 manipulation tasks in one day using a new efficient learning method.
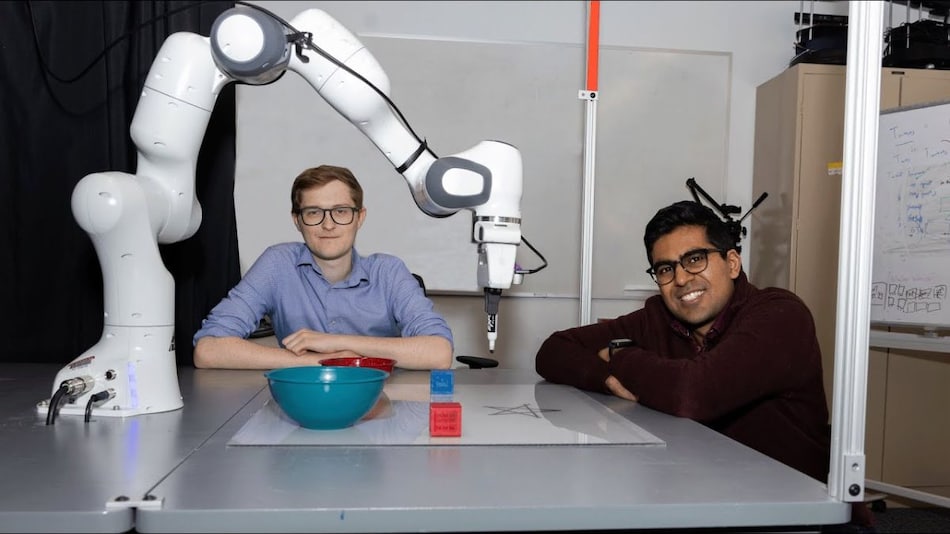

The robotic arm completes 1,000 tasks in a day using the MT3 imitation learning approach
Click Here to Add Gadgets360 As A Trusted Source

Scientists at Imperial College London have taught a robotic arm to complete 1,000 individual tasks, including using tools and lifting multiple objects in a single day, by training it for eight hours. By employing a novel imitation learning method, MT3 (multi-task trajectory transfer), we can enable the Sawyer robot to acquire any task and perform it from only one single demonstration, without the need for a large amount of training data. The approach combines trajectory decomposition with retrieval-based generalisation, enabling the robot to apply demonstrations to new objects and tasks. This advance could revolutionise how robots learn and perform multiple tasks efficiently.
New MT3 System Enables Robots to Learn Tasks from Single Demonstrations with High Accuracy and Adaptability
As per a report in Science Robotics, MT3 enables the robot to decouple each task into alignment and interaction phases and to re-select the most related demonstration from memory according to task description and environmental perception. This method guarantees correct behaviour without error, which makes the actions of a robot more explicable and trustworthy than traditional black-box deep learning.
The robot arm was able to learn new tasks from a single demonstration through motion adaptation via pose estimation and planning, resulting in an efficient, reliable pick‐and‐place of different objects.
MT3 Enables Data-Efficient, Interpretable Robot Learning, Paving the Way for Versatile Real-World Applications
This work shows that large-scale robot learning of complex tasks is achievable with neither huge datasets nor large neural networks. Researchers note that MT3 is a data-efficient and interpretable way to generalize within-class policies in comparison to behavioral cloning, allowing robots to deal with very diverse sets of skills with limited human provision.
Still more improvements in the future will allow robots to adjust trajectories for unseen objects, shortening training times and resources needed, and enabling flexible, effective real-world robotic systems.